Messier 102 (M102), also known as the Spindle Galaxy, is an edge-on lenticular galaxy located in the northern constellation Draco. The galaxy lies at a distance of 50 million light years from Earth and has an apparent magnitude of 10.7. It has the designation NGC 5866 in the New General Catalogue.
The Spindle Galaxy occupies an area of 4.7 by 1.9 arc minutes of apparent sky, corresponding to a linear extension of about 60,000 light years. It is very difficult to see with binoculars, but easily visible in small telescopes, which show a thin, nebulous patch under good conditions. 4-inch telescopes show a bright elliptical nebulous patch with a brighter core, while 6-inch and 8-inch instruments reveal a halo of light and hints of the galaxy’s dark dust lane. Larger telescopes show the galaxy’s well-defined bright centre and more details of its structure.
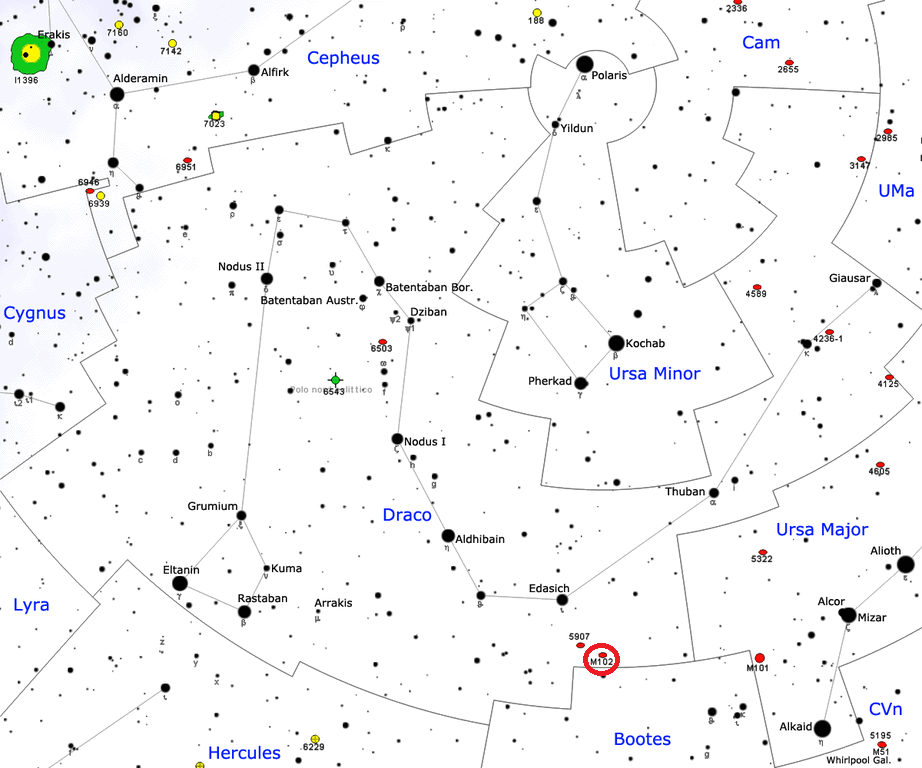
The Spindle Galaxy can be found east of the Big Dipper, in the southern part of Draco. It is located 4 degrees southwest of the magnitude 3.3 red giant star Edasich, Iota Draconis, in the direction of Alkaid, Eta Ursae Majoris, the star that marks the tip of the Big Dipper‘s handle. The best time of year to observe M102 is during the spring. Observers north of latitude 35N can see the galaxy throughout the year as it is circumpolar and never sets below the horizon.
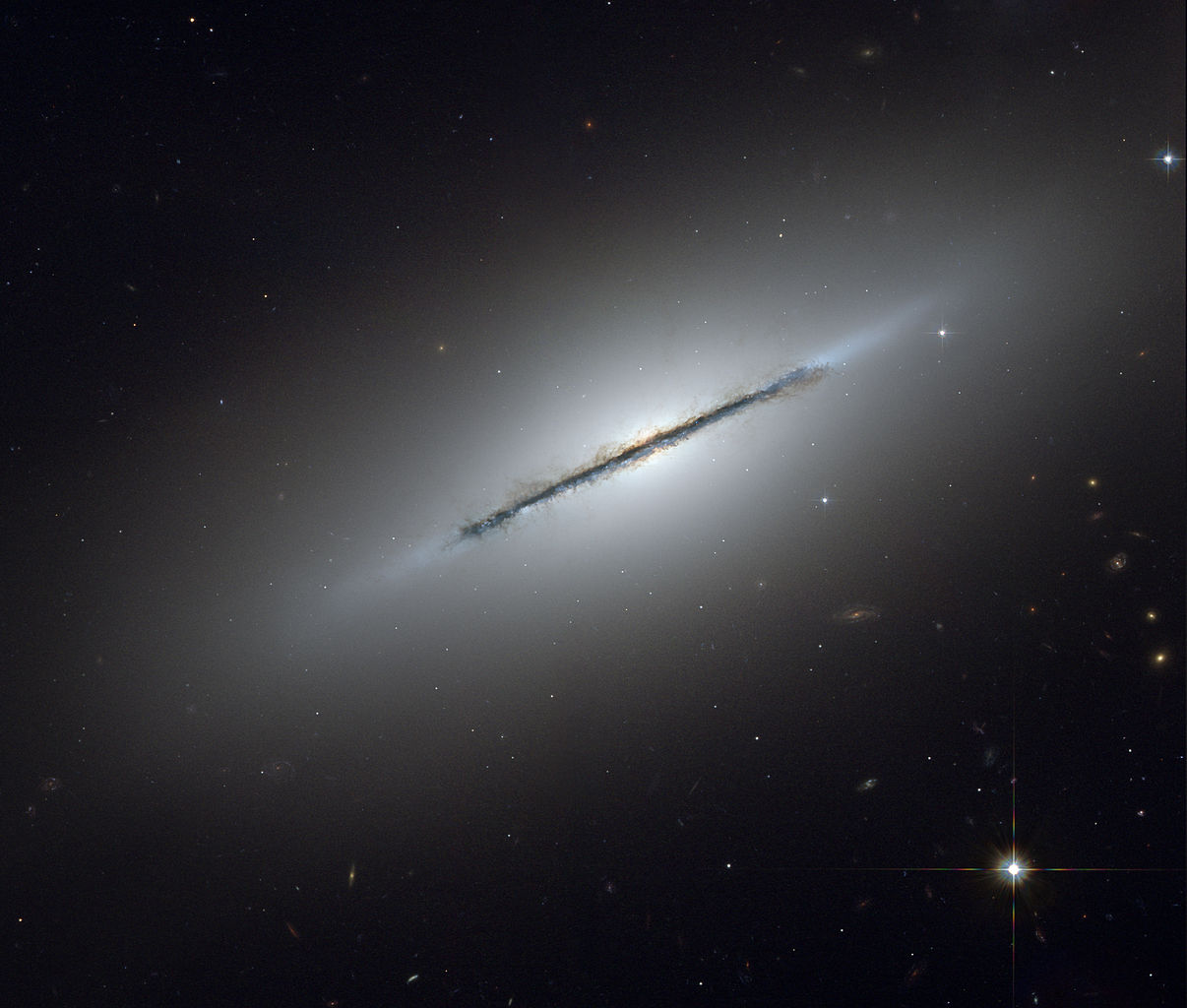

The Spindle Galaxy is estimated to contain 100 billion stars. It has a prominent extended central dust disk that appears almost exactly edge-on when seen from Earth. The dust disk is very unusual for a galaxy of this type. Lenticular galaxies typically have dust only near the central region and the dust follows the light profile of the galactic bulges.
The dust disk in M102 may contain a ring structure, but the shape of the structure is difficult to determine because the galaxy is seen edge-on. The galaxy may have been misidentified as a lenticular galaxy and may in fact be a spiral, which would make the dust disk far less unusual.
Messier 102 is receding from us at 672 km/s. The galaxy’s central dust lane appears slightly warped, indicating that M102 may have interacted with another galaxy in the distant past.
The Spindle Galaxy is one of the brightest members of the NGC 5866 Group, or M102 Group, a small group of galaxies that also includes the nearby NGC 5907, NGC 5879, NGC 5870, NGC 5866A and NGC 5866B, UGC 9776 and PGC 54577. Numerous fainter background galaxies can be seen in the same area of the sky, including the relatively bright pair NGC 5905/NGC 5908 and the galaxies NGC 5862, NGC 5867, NGC 5874, NGC 5876 and IC 1099.
The north celestial pole passes within a degree of M102 every 25,800 years. The galaxy last marked the location of the pole about 6,900 years ago, in 4900 BC, and will do so again in 18,900 years, around 20900 AD.
NGC 5866 is one of the two galaxies known as the Spindle Galaxy. The other, NGC 3115, is an edge-on lenticular galaxy located in the constellation Serpens.
The Spindle Galaxy was most likely discovered either by Pierre Méchain or Charles Messier in 1781. Méchain documented M102 in late March or early April, 1781, describing the object as a “nebula between the stars Omicron Boötis & Iota Draconis,” adding that “it is very faint; near it is a star of the sixth magnitude.” Méchain probably meant Theta Boötis, not Omicron, which contributed to the confusion around the identity of M102. Omicron Boötis is more than 40 degrees away from Iota Draconis, which makes the possibility of an error very likely.
Méchain reported the discovery to Messier, who added the object to his catalogue without providing a position. Messier later gave a handwritten position for M102 in his personal copy.
The Spindle Galaxy was independently discovered by William Herschel in 1788. Herschel determined the position of the object on May 5, 1788 and catalogued it as H I.215, describing it as “very bright. Considerably large. Extended. Following [east of] 2 stars.”
John Herschel catalogued the object as h 1909, but made a mistake in referring to it as William Herschel’s H I.219 instead of H 1.215. He described it as “very bright; pretty much elongated; gradually brighter toward the middle; 50″ long, 20″ broad; extended along position angle 326 [= 146] by micrometer.”
Herschel later corrected the error and included the object in his General Catalogue as GC 4058.
William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse, observed M102 on April 27, 1848 and offered the following description:
A very bright resolvable nebula, but none of the component stars to be seen distinctly even with a power of a thousand. A perfectly straight line and longitudinal division in the direction of the major axis. Resolvability most strongly indicated toward the nucleus.
French astronomer Camille Flammarion identified NGC 5866 as M102 in his “List of the Messier Objects,” published in L’Astronomie in November 1917, arguing that the Greek letter Omicron (ο), written down by Messier, was in fact a lowercase Theta (θ). This was probably correct because the object found at this location corresponds to Messier’s description of M102.
Harlow Shapley and Helen Davies commented on the identification of M102 in 1917, pointing out the following:
By a star chart, or the sky, you will see that, taken as it stands, no object could be well selected for M102, since Omicron Boötis is too far from Iota Draconis. If, however, Omicron is a misprint for Theta, it becomes intelligible, and M102 is perhaps N.G.C. 5866, altho in Norton’s Atlas it is apparently identified as N.G.C. 5979. On our photographs, however, N.G.C. 5866 appears to be the brightest object in this region.”
Heber Curtis photographed M102 with the Crossley telescope at the Lick Observatory and noted:
Very bright, 3’x1′ in p.a. 125deg. No spiral structure is discernible, but it appears to be a spiral of the Andromeda type seen edgewise. Its most striking feature is a narrow, clear-cut dark lane along the middle, marking a slight angle with the major axis.
M102 controversy
The Spindle Galaxy is an object that closely matches both the position given by Charles Messier and the description provided by Pierre Méchain, who discovered M102. However, in a letter written to J. Bernoulli on May 6, 1783, Méchain stated that M102 was a duplicate observation of the Pinwheel Galaxy (M101) in Ursa Major, and for this reason the Spindle Galaxy has not been conclusively identified as M102. Méchain wrote, “I will add only that No. 101 & 102 on the p. 267 of the Connoissance des temps 1784 are nothing but the same nebula, which has been taken for two, by an error in the charts.”
However, NGC 5866 was most likely the object that Messier observed when he determined the position for M102. It is almost exactly 5 degrees west of the position given for M102, which is probably a result of a data reduction error.
In addition to M101 and NGC 5866, several other galaxies have been suggested as candidates for M102 by different astronomers and historians. The galaxies NGC 5879 (mag. +12.4), NGC 5905 (mag. +12.1), the Splinter Galaxy (NGC 5907, mag. +11.1) and NGC 5908 (mag. +12) are all located in the vicinity of NGC 5866, but none of them are as bright and they all have a lower surface brightness, which makes them less likely to be the object seen by Méchain and Messier. All four of these galaxies are spirals.
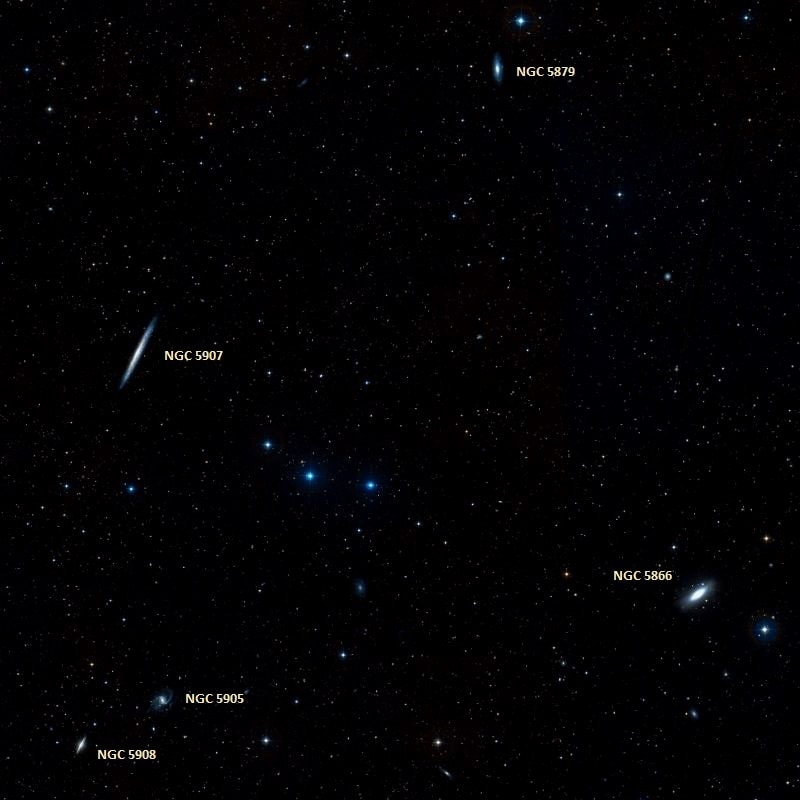

NGC 5905 and NGC 5908 lie at an approximate distance of 140 million light years from Earth and are separated by about 500,000 light years. NGC 5905 appears face-on and NGC 5908 is seen edge-on and bears a striking resemblance to the Sombrero Galaxy (M104), a famous edge-on spiral in Virgo constellation. The Splinter Galaxy (NGC 5907) is another edge-on spiral located approximately 50 million light years away.
NGC 5928, a 14th magnitude galaxy located in Serpens constellation, between the stars ο Boötis and ι Serpentis, was proposed as a candidate for M102 by John Louis Emil Dreyer, the Danish-Irish astronomer who compiled the New General Catalogue based on William Herschel’s catalogue. Dreyer based his suggestion on the possibility that ι Serpentis may have been misidentified as ι Draconis in the position given for M102. He wrote:
NGC 5928. This is possibly Messier 102, found by Méchain: “Nébuleuse entre les étoiles Omicron du Bouvier et Iota du Dragon: elle est très foible; pres d’elle est une étoile de la sixième grandeur.” I assume that Iota Draconis is an error for Iota Serpentis.
However, NGC 5928 is not a likely candidate because it may not even have been observable by Méchain and Messier.
FACTS
| Object: Galaxy |
| Type: Lenticular |
| Class: S0 |
| Designations: Messier 102, M102, NGC 5866, Spindle Galaxy, PGC 53933, UGC 9723, 1E 1505.1+5557, IRAS 15051+5557, 2MASX J15062956+5545479, MCG+09-25-017, UZC J150629.4+554548, Z 274-16, Z 1505.1+5557 |
| Features: Extended dust disk |
| Constellation: Draco |
| Right ascension: 15h 06m 29.5s |
| Declination: +55°45’48” |
| Distance: 50 million light years (15.3 megaparsecs) |
| Number of stars: 100 billion |
| Apparent magnitude: +10.7 |
| Apparent dimensions: 4′.7 x 1′.9 |
| Radius: 30,000 light years (9,200 parsecs) |
| Redshift: 672 km/s |
LOCATION